Ecg Trace Explained. I don t do this because it can alter the patient s heart rate. The electrocardiogram ecg or ekg is a diagnostic tool that is routinely used to assess the electrical and muscular functions of the heart. A 12 lead ecg records 12 leads producing 12 separate graphs on a piece of ecg paper. An ecg electrode is a conductive pad which is attached to the skin to record electrical activity.
Some paramedics ask patients to hold their breath while they capture a 12 lead ecg. For example if you are wanted an ecg to look for changes of hyperkalaemia note the patient s potassium level on the ecg. I don t do this because it can alter the patient s heart rate. While it is a relatively simple test to perform the interpretation of the ecg tracing requires significant amounts of training. Or other relevant clinical details. An ecg lead is a graphical representation of the heart s electrical activity which is calculated by analysing data from several ecg electrodes.
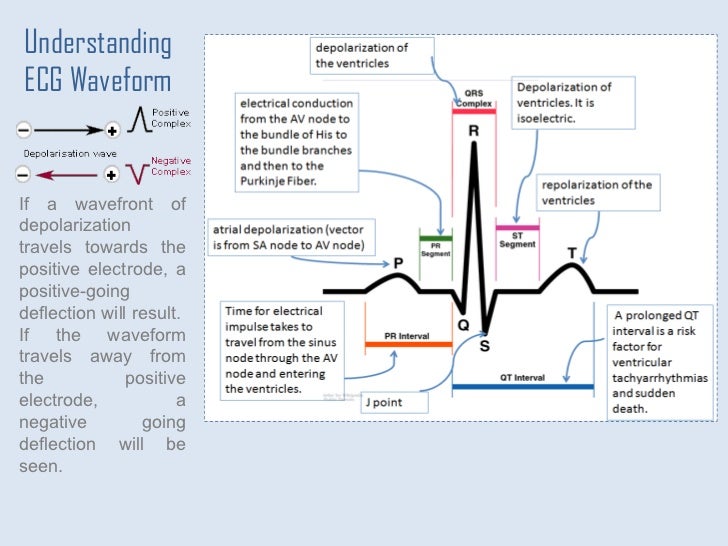
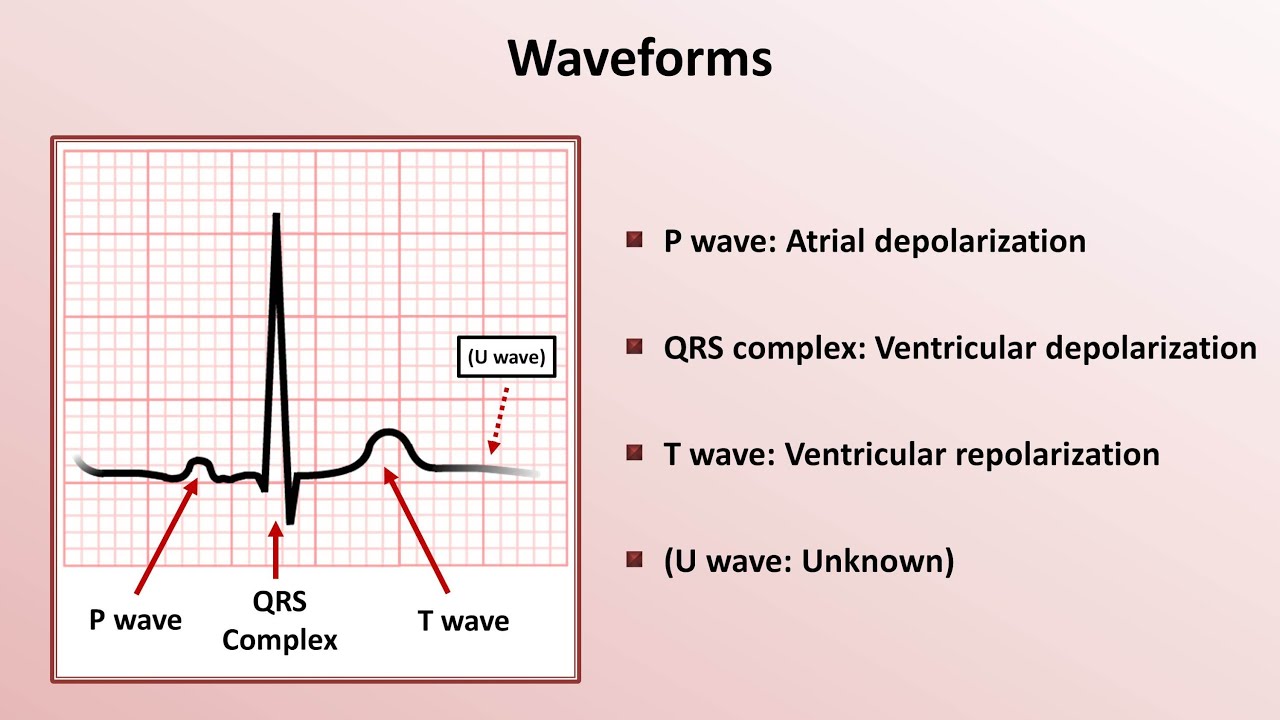
The different waves that comprise the ecg represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles.
There are times when your patient is acutely short of breath and it s simply impossible to capture a 12 lead ecg with excellent data quality. Count the number of qrss on one line of the ecg usually lead ii running along the bottom and multiply. Or other relevant clinical details. The ecg is recorded at a speed of 25 mm sec 5 large squares sec and the voltages are calibrated so. The ekg is a printed capture of a brief moment in time. While it is a relatively simple test to perform the interpretation of the ecg tracing requires significant amounts of training.