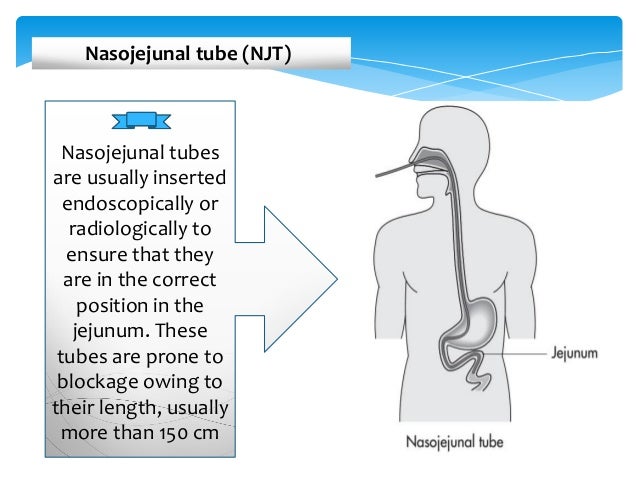
Nasojejunal Feeding Tube Placement. The indications for nasojejunal tube placement included gastroesophageal reflux disease gerd in 10 patients gastroparesis in five feeding intolerance in four patients and hemorrhagic gastritis pancreatitis and decompression for intestinal pseudoobstruction in one patient each. Significant complications due to nasojejunal feeding tube placement such as hydrothorax duodenal. Nasojejunal tube njt thin soft tube passed through a patient s nose down the back of the throat through the oesophagus stomach and pyloric sphincter into the jejunum. Percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy pej a feeding tube which is inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach and then extends into the jejunum.
Experience with fluoroscopically guided nasojejunal feeding tube placement in children was assessed regarding clinical diagnosis fluoroscopy time radiation dose success rate and placement failures. Significant complications due to nasojejunal feeding tube placement such as hydrothorax duodenal. Nasojejunal tube njt thin soft tube passed through a patient s nose down the back of the throat through the oesophagus stomach and pyloric sphincter into the jejunum. From 1987 to 1991 562 nasojejunal tubes were placed in 232 patients aged 1 week to 24 years mean 3 1 2 years. Nasojejunal feeding tube placement can be achieved by fluoroscopic or endoscopic techniques. From 1987 to 1991 562 nasojejunal tubes were placed in 232 patients aged 1 week to 24 years mean 3 1 2 years at the authors institution.
The indications for nasojejunal tube placement included gastroesophageal reflux disease gerd in 10 patients gastroparesis in five feeding intolerance in four patients and hemorrhagic gastritis pancreatitis and decompression for intestinal pseudoobstruction in one patient each.
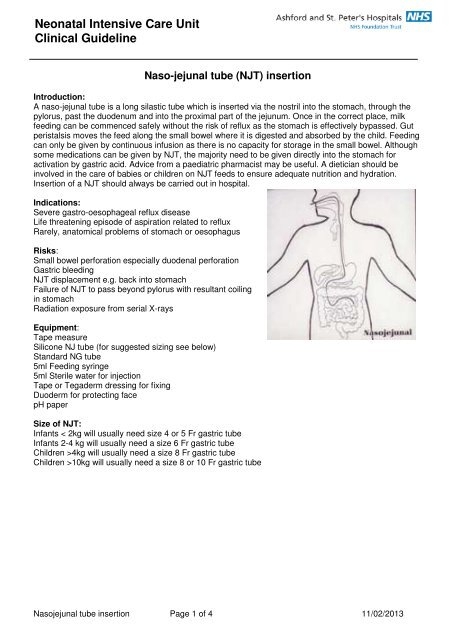
The indications for nasojejunal tube placement included gastroesophageal reflux disease gerd in 10 patients gastroparesis in five feeding intolerance in four patients and hemorrhagic gastritis pancreatitis and decompression for intestinal pseudoobstruction in one patient each. Nasojejunal feeding tube placement can be achieved by fluoroscopic or endoscopic techniques. Gerd was diagnosed with 24 hour ph monitoring. Nasojejunal tube njt thin soft tube passed through a patient s nose down the back of the throat through the oesophagus stomach and pyloric sphincter into the jejunum. From 1987 to 1991 562 nasojejunal tubes were placed in 232 patients aged 1 week to 24 years mean 3 1 2 years. Percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy pej a feeding tube which is inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach and then extends into the jejunum.