Placement Of Peg Tube. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy is an endoscopic medical procedure in which a tube is passed into a patient s stomach through the abdominal wall most commonly to provide a means of feeding when oral intake is not adequate. Antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated to prevent skin site infection. A percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy peg tube is a feeding tube surgically placed through your abdomen into your stomach. Peg tube placement should be carried out under full aseptic technique.
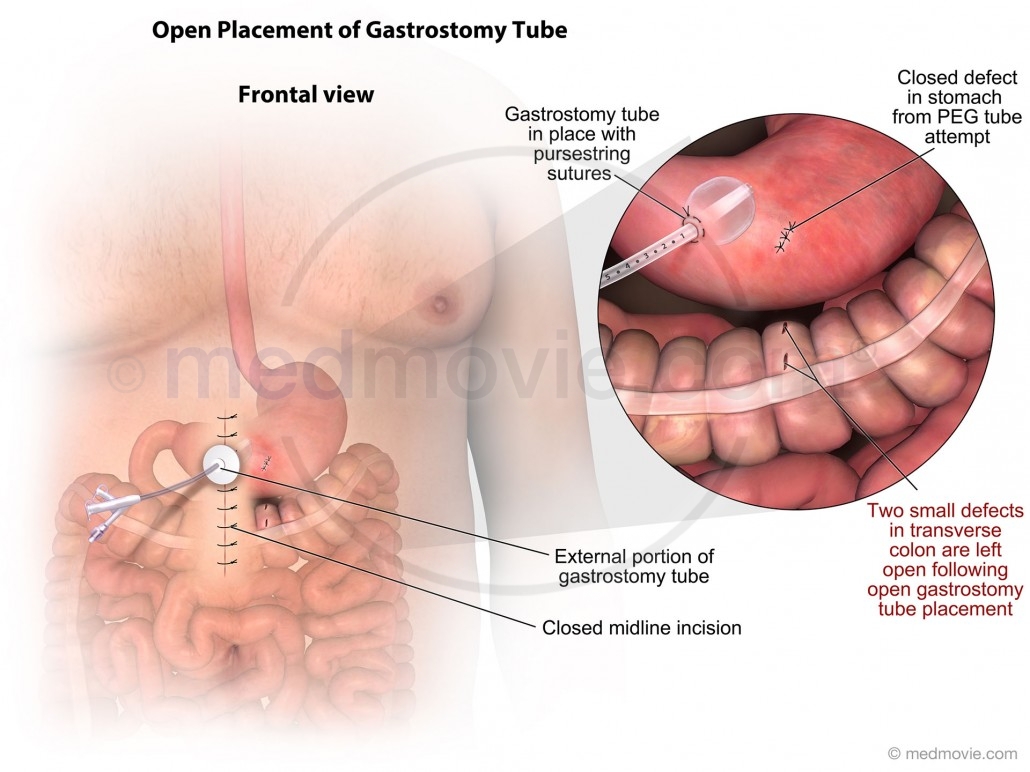
In areas of high meticillin resistant staphylococcus aureus mrsa prevalence oro pharyngeal colonisation should be identified and managed prior to peg tube placement. Your surgeon cuts through the skin of your belly and inserts the tube right into your stomach to deliver a liquid food mixture or a formula. The endoscope lets your healthcare provider see inside your stomach as the procedure is done. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy peg is a surgical procedure for placing a tube for feeding without having to perform an open operation on the abdomen laparotomy. It is used in patients who will be unable to take in food by mouth for a prolonged period of time. The peg procedure is an alternative to open surgical gastrostomy insertion and does not require a general anesthetic.
During the peg tube placement procedure a physician places an endoscope a long thin flexible instrument about 1 2 inch in diameter into your mouth.
In areas of high meticillin resistant staphylococcus aureus mrsa prevalence oro pharyngeal colonisation should be identified and managed prior to peg tube placement. Peg tube placement should be carried out under full aseptic technique. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy peg is a method of placing a tube into the stomach percutaneously aided by endoscopy. Your surgeon cuts through the skin of your belly and inserts the tube right into your stomach to deliver a liquid food mixture or a formula. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy is an endoscopic medical procedure in which a tube is passed into a patient s stomach through the abdominal wall most commonly to provide a means of feeding when oral intake is not adequate. It s placed using a lighted flexible scope called an endoscope.