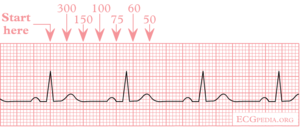
Reading Ekg Rate. Count the number of large squares present within one r r interval. Heart rate what s a normal adult heart rate. Heart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares and that s it. Ekg tracing please refer to the ekg tracing below if you are not familiar with the labeling of the ekg waveforms.
Heart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares and that s it. There are multiple methods to estimate the rate. Although heart rate can be calculated easily by taking a pulse studies show that an ecg electrocardiogram may be necessary to determine if there is any damage to the heart how well a device or drug is working whether the heart is beating normally or to determine the location and size of the heart chambers. Then count either forward or. For example if there are 7 r waves in a 6 second strip the heart rate is 70 7x10 70. 5 small squares 1 large square 0 2 seconds.
On the ekg locate a r wave that matches a thick line count the number of large squares to the next r wave.
5 large squares 1 second. 1500 small squares 300 large squares 1 minute. With the paper speed of 50 mm s one minute equals a strip length of 3 000 mm or 600 large squares 1 large square equals 5 mm. Count the number of spikes that are in a 6 second readout and multiply the number by 10 to get an approximate rate. Alternately you can count the complexes on the rhythm strip which represents 10 seconds. This means that if the interval between two beats r r is 5 large squares the hr is 60 beat min.