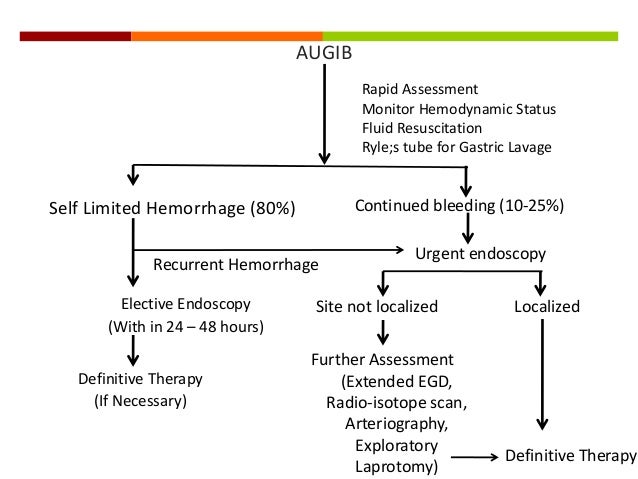
Upper Gi Bleed Management. Blood transfusions generally should be administered to patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding who have a hemoglobin level of 7 g per dl 70 g per l or less. It involves working through the following steps. The abcde approach can be used to perform a systematic assessment of a critically unwell patient. It aims to identify which diagnostic and therapeutic steps are useful so hospitals can develop a structure in which clinical teams can deliver an optimum service for people who develop this condition.
This guide provides an overview of the recognition and immediate management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding ugib using an abcde approach. Among the changed recommendations. The most common manifestation of ugib is melena or hematemesis. Once identified therapeutic endoscopy can achieve acute hemostasis and prevent recurrent bleeding. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is a common medical emergency worldwide and refers to bleeding from the esophagus stomach or duodenum. Upper endoscopy is the first choice for acute upper gi bleeding and has a high sensitivity for locating and identifying bleeding lesions in the upper gi tract.
Once identified therapeutic endoscopy can achieve acute hemostasis and prevent recurrent bleeding.
This guideline covers how upper gastrointestinal bleeding can be effectively managed in adults and young people aged 16 years and older. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding ugib is a common medical condition with various etiologies and presentations. Once identified therapeutic endoscopy can achieve acute hemostasis and prevent recurrent bleeding. The interdisciplinary management of gastrointestinal gi bleeding involves volume resuscitation correction of coagulation disorders and protection of the airway while initiating diagnostic procedures to determine the site of bleeding. Rapid assessment stabilization and resuscitation should precede all diagnostic modalities in unstable children. The abcde approach can be used to perform a systematic assessment of a critically unwell patient.